|
Mainland Geography
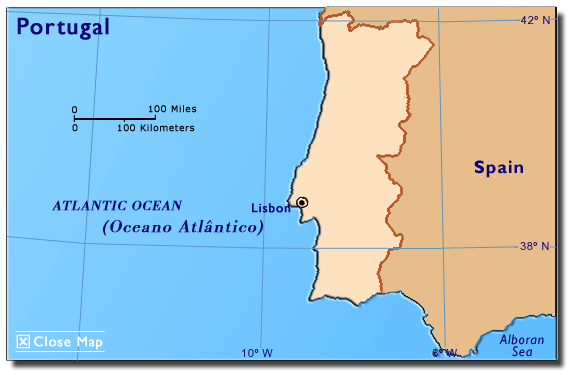
 Portugal is the closest eastern neighbor of the United States, and, in addition to the mainland, includes the autonomous regions of the Azores and Madeira archipelagos. Mainland Portugal, (Portugal, 2005) located on the Iberian Peninsula (Europe, 2002) in southwest Europe, shares its northern and eastern borders with Spain; the Atlantic Ocean lies to the west and south.
Portugal is the closest eastern neighbor of the United States, and, in addition to the mainland, includes the autonomous regions of the Azores and Madeira archipelagos. Mainland Portugal, (Portugal, 2005) located on the Iberian Peninsula (Europe, 2002) in southwest Europe, shares its northern and eastern borders with Spain; the Atlantic Ocean lies to the west and south.
The mainland area is 35,515 square miles (91,985 sq. kilometers) or about the size of the state of Indiana. Mountains and high plateaus dominate the northern mainland. The south is mostly rolling countryside and plains. Many rivers cross the country, of which the Tagus (Tejo) is the longest. Portugal has large forests and an 1114-mile (1,793-kilometer) coastline (Geography of Portugal, 2004).
Climate
Mainland Portugal has two main climate zones (Geography of Portugal, 2004). The northern zone is cool and rainy influenced by Atlantic air currents and the Spanish Meseta. The southern zone is warmer and drier, influenced by the Mediterranean climate with low precipitation and sunny weather conditions.
History
Portugal (History of Portugal, 2005) is one of the oldest nation states of Europe, and the foundation of the country predates that of neighboring Spain by nearly 350 years (Marques, 1991) . The Portuguese people descend from ancestral Iberian tribes and other ancient peoples such as the Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians, Greeks, Visigoths, Romans, and Moors as well as Jewish settlers (Mausenbaum, 2003).
Portugal became an independent kingdom (The Establishment of the Monarchy in Portugal, 2003) in 1143 under D. Afonso Henriques (Alphonso I ) who is credited with the capture of Lisbon from the Moors in 1147 (The Establishment of the Monarchy in Portugal, 2003). In the 15th century, Prince Henry (Henry the Navigator, 2004), also known as Henry the Navigator, initiated a period of maritime exploration with the discovery of Madeira in 1418, followed by the discovery of the Azores (Azores, 2005) in 1427. Cape Verde was reached in 1460 and Brazil in 1500 (República da Cabo Verde, n.d.). In 1497, Vasco da Gama (2004) led the first European sea expedition to India reaching what is now known as Calcutta in 1499 thus discovering the sea route to India (Birmingham, 1993; Boxer, 1991) .
The Portuguese overseas empire expanded to include land holdings and trading posts in Africa, South America, Middle East, India, Japan and China. Although the Portuguese Empire lasted over five centuries, the independence of Brazil, in 1822, heralded its decline. In 1999, the last of its territorial holdings, Macao reverted to China (Russell-Wood, 1993) .
Modern Portuguese history is marked by the overthrow of the monarchy in 1910, the establishment of civilian rule, and long periods of social unrest (Manuel II of Portugal, 2004). In 1926, a military coup overthrew the civilian government. In 1932, an authoritarian dictatorship led by António de Oliveira Salazar (Antonio de Oliveira Salazar, 2004), was installed and continued until the Carnation Revolution of 25th of April of 1974 (Carnation Revolution, 2003), which overthrew the old regime and established a parliamentary democracy (Manuel, 1996; Opello, 1991) . In 1986, Portugal joined the European Union (Europa, n.d.b) and has since enjoyed increasing economic growth and political stability (Magone, 1997) .
Political Organization
 Portugal is a constitutional democracy. The central administration is organized in 18 administrative districts , which comprise the mainland (Districts of Portugal, 2004). The Madeira and the Azores archipelagos are Autonomous Regions (Symington, 2000) . The Portugal Republic is ruled by a Constitution that provides for a system with four sovereign organs (Portal do Governo, n.d.). The President is the Chief of State and represents the Portuguese Republic (Sampaio, n.d.). The Prime Minister (Porto do Governo, n.d.b) is the head of the Government (Porto do Governo, n.d.a), which is the organ that is responsible for the development, and implementation of national policies and the highest authority for the purpose of public administration. Portugal is a constitutional democracy. The central administration is organized in 18 administrative districts , which comprise the mainland (Districts of Portugal, 2004). The Madeira and the Azores archipelagos are Autonomous Regions (Symington, 2000) . The Portugal Republic is ruled by a Constitution that provides for a system with four sovereign organs (Portal do Governo, n.d.). The President is the Chief of State and represents the Portuguese Republic (Sampaio, n.d.). The Prime Minister (Porto do Governo, n.d.b) is the head of the Government (Porto do Governo, n.d.a), which is the organ that is responsible for the development, and implementation of national policies and the highest authority for the purpose of public administration.
The Parliament (Assembleia da República, n.d.) known as the Assembleia da República is unicameral and seats 230 deputies elected by secret ballot and popular vote, including representatives from the Autonomous Regions of Madeira and the Azores (Bruneau, 1997) . The judicial branch of the Portugal Republic comprises a constitutional review court and three levels of judicial forums (courts of first instance, courts of appeal and a Supreme Court) that are independent and subject only to the law (European Judicial Network, 2003). All persons can seek relief for the violation of any legal rights regardless of financial circumstances and are entitled to proper representation by a lawyer.
Economy
Portugal has a capitalist economy (Economy of Portugal, 2003). It has been a member of the European Union (EU) since 1986, and the economy has become “divers ified and increasingly servic ebased” (The World Bank Group, 2003). In 2002 along with eleven other European countries, it began to circulate the “Euro” as its currency. The estimated Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2002 was $182 billion with a per capita GDP of $18,000. Portugal has enjoyed steady growth rates, low inflation and unemployment.
The country produces the following agricultural products : grapes, grain, potatoes, olives, dairy products, sheep, goats, cattle, and poultry (Economy of Portugal, 2003). Portugal exports clothing and footwear, machinery, chemicals, cork, paper products and hides. Major industries include winemaking, fisheries, hydropower, textiles, clothing, paper, cork, footwear, metalworking, oil refining, chemicals, food processing, and tourism. Portuguese Port wines and Madeira wines are world renown (Economy of Portugal, 2003).
|